Adipose Tissue: Functions, Types, and Its Role in Your Health
-
PepEurope
- Posted on
- 0 comments
Adipose tissue, also known as body fat, is far more than just stored energy or unwanted weight gain. It is a specialized connective tissue that plays essential roles in maintaining balance and overall health. In healthy adults, adipose tissue typically accounts for about 20% to 25% of total body weight, depending on age, gender, and lifestyle.
While fat often has a negative reputation, it is crucial for survival because it helps regulate hormones, protects vital organs, and maintains body temperature. Understanding body fat allows us to appreciate its importance in health, as well as the risks associated with having too much or too little of it.
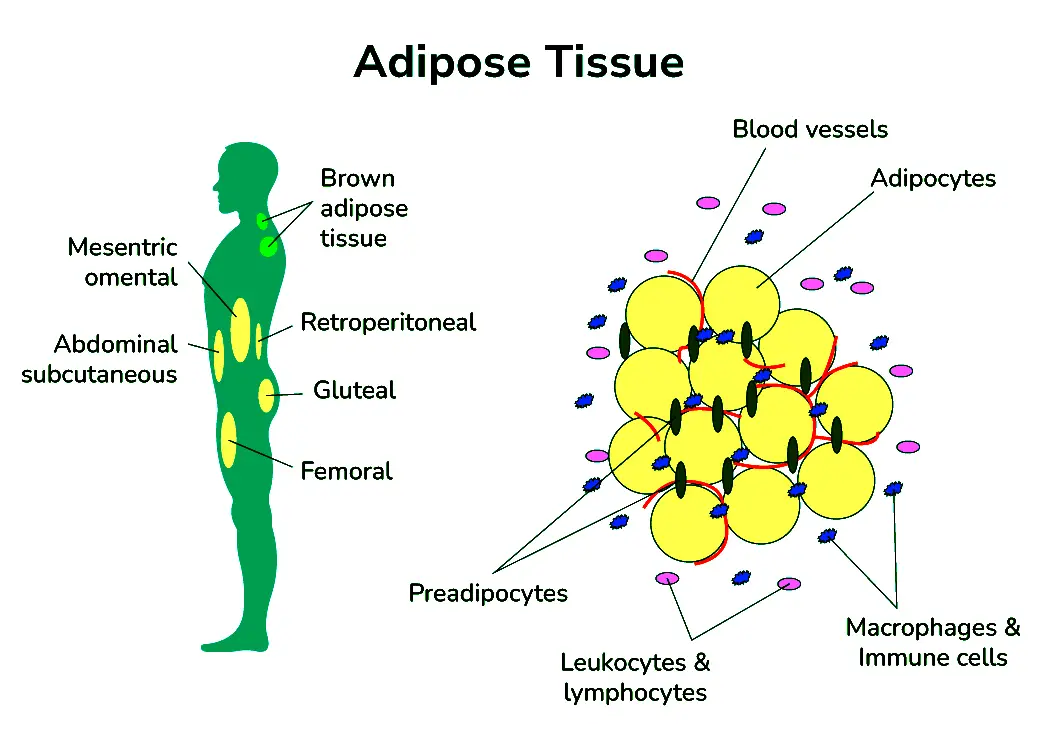
Structure and Location of Adipose Tissue
Adipose tissue is mainly made up of fat cells called adipocytes. These cells store energy in the form of lipids and can expand or shrink depending on how much fat they hold. But the body fat isn’t just fat cells it also contains blood vessels, immune cells, and connective fibers that support its function.
It is found throughout the body in different places:
- Subcutaneous fat – under the skin, helping insulate and cushion the body.
- Visceral fat – deeper fat surrounding organs like the heart, liver, and kidneys.
- Other sites – bone marrow, around the eyes, heart, and even the soles of the feet.
The location of fat matters a lot, since visceral fat carries more health risks compared to subcutaneous fat.
Reta Support Formula 20 (GLP-1 + GIP + GCGR)
3 x RETA 20mg PACK
Tesofensine Supplements (Weight Loss/Neurotransmission)
Types of Adipose Tissue and Their Roles
There are three main types of adipose tissue (White, Brown & Beige adipose tissue), each with unique roles. White adipose tissue is the most abundant in adults and serves as the primary storage site for energy while also providing insulation and cushioning for organs.
Brown adipose tissue, on the other hand, is more common in newborns and plays an important role in producing heat to protect against cold temperatures.
Although it diminishes with age, small amounts remain in adults and can still help burn calories through thermogenesis. The third type, beige adipose tissue, is a hybrid that shares characteristics of both white and brown fat.
Beige fat is especially interesting to researchers because it has the potential to burn energy like brown fat, which may help in managing obesity and metabolic disorders.
Main Functions of Adipose Tissue
Adipose tissue performs a wide variety of vital functions that extend far beyond simply storing fat. One of its main roles is energy storage and release. When we consume more calories than we need, adipocytes store the excess energy as fat, which can later be released when the body requires fuel. Adipose tissue also plays a role in temperature regulation, especially through brown and beige fat, which generate heat in cold environments.
Another crucial function is its role as an endocrine organ, as fat cells release hormones such as leptin, which signals satiety to the brain, and adiponectin, which improves metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Additionally, adipose tissue cushions internal organs, acting as a protective layer against mechanical stress, while also supporting immune function by hosting immune cells that help fight infections and manage inflammation.
Endocrine and Metabolic Roles of Adipose Tissue
Adipose tissue communicates with other organs in the body through hormones and chemical messengers, making it a highly active part of the endocrine system. The hormone leptin, for example, helps regulate appetite by signaling to the brain when the body has had enough food, while adiponectin supports healthy metabolism and helps the body use insulin more effectively. When the body fat is functioning properly, it helps balance blood sugar levels, regulate appetite, and maintain metabolic health.
However, when there is too much visceral fat, these functions can be disrupted, leading to conditions such as insulin resistance, diabetes, and heart disease. This highlights the delicate balance required for the body fat to support rather than harm overall health.
Reta Support Formula 20 (GLP-1 + GIP + GCGR)
3 x RETA 20mg PACK
Tesofensine Supplements (Weight Loss/Neurotransmission)
Clinical Relations
Problems with adipose tissue can lead to a number of health conditions:
- Obesity: Too much the body fat increases the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and fatty liver.
- Lipodystrophy: A rare condition where the body has too little or abnormal fat distribution, which also causes health issues.
- Type 2 diabetes: Strongly linked to excess visceral fat.
- Cardiovascular disease: Fat around organs can disrupt heart and blood vessel function.
In short, both too much and too little adipose tissue can cause health problems, which is why balance is key.
Risk Factors That Affect Adipose Tissue Health
Several factors influence how adipose tissue develops and functions in the body. Diet and physical activity play a major role, as consuming more calories than the body can burn leads to fat buildup, while regular exercise helps reduce harmful fat stores. Genetics also influence fat distribution, as the number of fat cells in the body is largely set during childhood and adolescence.
Once formed, fat cells rarely disappear, which is why early prevention of obesity is so important. Hormonal imbalances, including those involving insulin, cortisol, and sex hormones, can also affect how and where fat is stored. Aging further contributes to changes in the body fat, often leading to increased visceral fat, which poses higher health risks.
Recent Research and Interesting Facts
Scientific research continues to reveal fascinating insights into the body fat. For example, the gut microbiome may influence fat storage and metabolism, with certain bacterial by-products helping regulate insulin sensitivity. Researchers have also discovered that excessive fat can create an inflammatory environment that encourages tumor growth, linking obesity to certain types of cancer.
Epigenetics, which involves changes in how genes are expressed, also plays a role in fat function and the development of metabolic disorders, offering potential new treatment options. Another area of growing interest is the role of brown adipose tissue in adults. Studies suggest that activating brown fat may help fight obesity by increasing the body’s ability to burn calories and generate heat.
How to Maintain Healthy Adipose Tissue
The good news is that we can take steps to keep our adipose tissue healthy:
- Balanced diet: Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity reduces white fat and helps activate brown and beige fat.
- Good sleep & stress control: Both affect hormone balance and fat distribution.
- Regular checkups: Monitoring BMI and waist-to-hip ratio helps track fat-related health risks.
Healthy lifestyle choices not only help manage weight but also keep fat tissue functioning properly.
Reta Support Formula 20 (GLP-1 + GIP + GCGR)
3 x RETA 20mg PACK
Tesofensine Supplements (Weight Loss/Neurotransmission)
FAQs About The Adipose Tissue
What is the main function of adipose tissue?
The primary function of adipose tissue is to store energy in the form of fat, but it also regulates body temperature, protects organs, and acts as an endocrine organ.
What are the different types of adipose tissue?
The three main types are white, which stores energy; brown, which generates heat; and beige adipose tissue, which has characteristics of both.
Why is visceral fat more dangerous than subcutaneous fat?
Visceral fat surrounds internal organs and increases the risk of serious conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and inflammation, whereas subcutaneous fat mainly insulates and cushions the body.
Can adults increase their brown adipose tissue?
Yes, research suggests that exposure to cold, regular physical activity, and certain diets may help activate brown fat in adults, boosting calorie burning.
How does adipose tissue act as an endocrine organ?
Adipose tissue releases hormones such as leptin and adiponectin, which regulate appetite, metabolism, and insulin sensitivity, influencing many aspects of health.
What are the risks of having too little adipose tissue?
Too little fat can lead to hormonal imbalances, weakened immunity, fertility issues, and higher risks of metabolic problems, showing that both extremes can be harmful.
Conclusion
Adipose tissue is often misunderstood as being simply excess body fat, but in reality, it is a highly dynamic and essential tissue that plays critical roles in energy storage, hormone regulation, organ protection, and temperature control. Both an excess and a deficiency of adipose tissue can negatively affect health, which is why balance is essential.
Advances in research continue to show how complex and important adipose tissue really is, from its influence on metabolism and immunity to its role in chronic diseases. By making mindful choices around diet, exercise, sleep, and stress, we can support the healthy functioning of adipose tissue and protect our overall health for the long term.
Are You Struggling to Lose Weight Despite Diet and Exercise?
Many people face the frustrating challenge of stubborn fat that just won't budget, even with strict diets and rigorous workouts. This is often due to slow metabolism, hormonal imbalances, or difficulty burning fat efficiently.
So, what's the solution?
Weight loss peptides offer a cutting-edge approach backed by research. These peptides help boost metabolism, regulate appetite, and promote fat burning naturally. By targeting the root causes of weight gain, peptides can accelerate your fat loss journey safely and effectively.
At PepEurope Ltd, we provide high-quality, scientifically formulated weight loss peptides designed to help achieve fitness goals faster and maintain a healthy, sustainable weight. Remember to use peptides only for research, not for consumption.