Aplastic Anemia – Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
-
PepEurope
- Posted on
- 0 comments
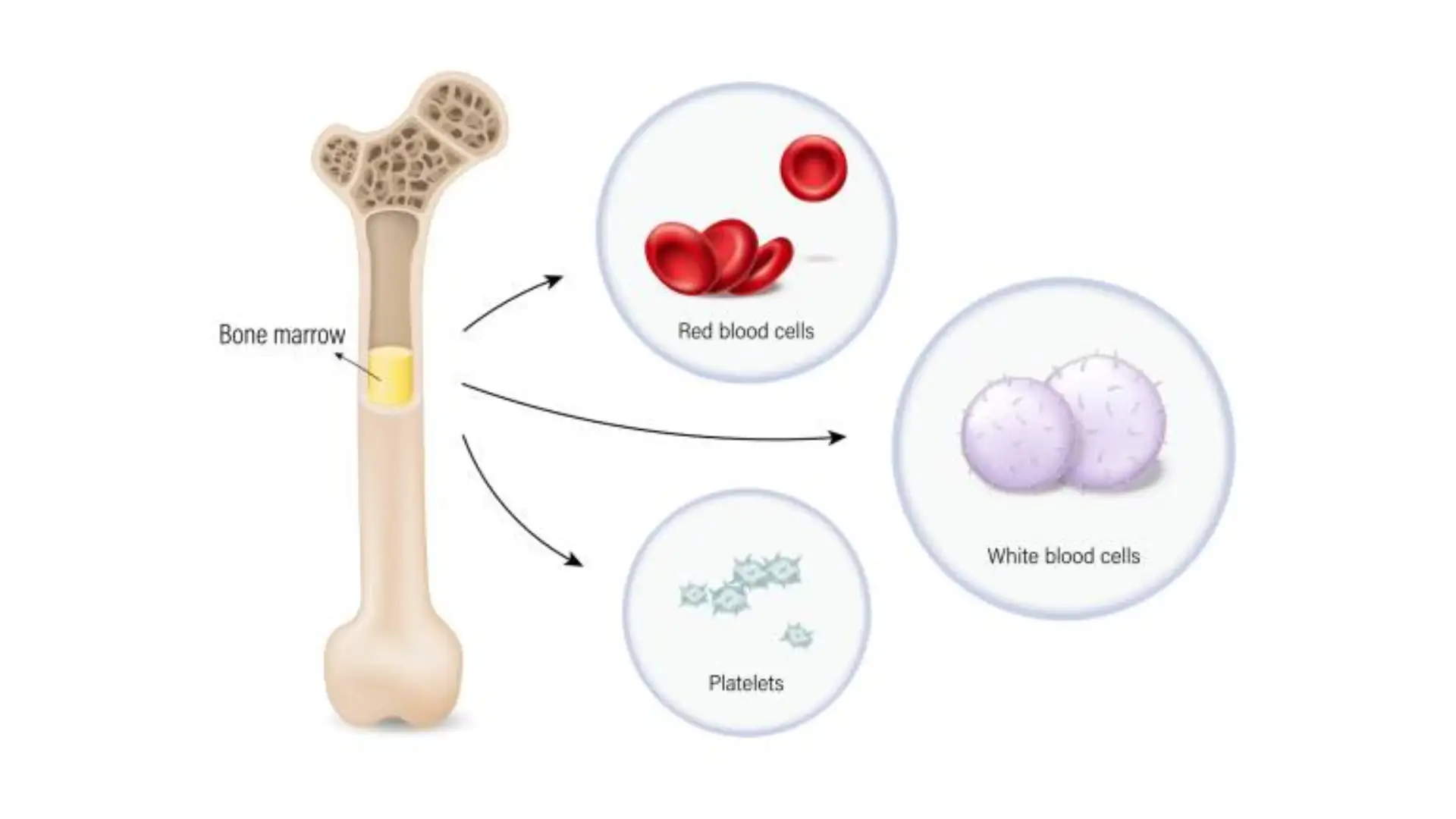
Aplastic anemia is a rare but serious blood disorder that poses a significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Despite its rarity, it is worth knowing its symptoms because they can vary and significantly affect daily functioning.
What is aplastic anemia?
Aplastic anemia is a condition in which the bone marrow does not produce enough of the essential blood cells – red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. The deficiency of these cells leads to reduced oxygen transport, weakened immunity and impaired blood clotting.
The disease can occur in various forms and degrees of advancement. The most common is idiopathic aplastic anemia, in which the immune system mistakenly attacks bone marrow stem cells, reducing blood cell production. Another form is secondary aplastic anemia, caused by external factors such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, viral infections or exposure to toxic substances. The disease may appear suddenly in acute form, which constitutes an immediate threat to life, or develop gradually as chronic form, with symptoms worsening over time.
Causes of aplastic anemia
The main cause of aplastic anemia is damage to the bone marrow, which disrupts the normal production of blood cells. Factors leading to this disease include:
- Genetic predisposition – Some people may have a hereditary tendency to develop aplastic anemia.
- Viral infections – Viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus or hepatitis viruses can trigger an autoimmune reaction leading to bone marrow damage.
- Medicines – Some pharmacological agents, including anticancer drugs and antibiotics, can have a toxic effect on bone marrow cells.
- Exposure to chemicals – Pesticides, heavy metals and other environmental toxins increase the risk of developing aplastic anemia.
MONTHLY SET NAD + -> Energy and Vitality Boost
Symptoms of aplastic anemia
Aplastic anemia presents with a variety of symptoms that can become more severe as the disease progresses. The most common symptoms include:
- Chronic fatigue and weakness – A result of reduced oxygen transport due to a deficiency in red blood cells.
- Pale skin – Caused by anemia.
- Dizziness, headaches and heart palpitations – The effect of insufficient oxygen circulation.
- Easy bruising and prolonged bleeding – The result of a low number of platelets, which are responsible for blood clotting.
- Frequent infections – A weakened immune system due to a deficiency in white blood cells increases susceptibility to infections.
Because these symptoms may resemble other diseases, it is necessary to consult a doctor promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis of aplastic anemia
Diagnosing aplastic anemia requires a series of tests to assess blood cell levels and bone marrow health. Basic diagnostic steps include:
- Blood count (CBC) – Measurement of red and white blood cell and platelet levels.
- Bone marrow biopsy – Analysis of bone marrow status to confirm the diagnosis.
- Immunological tests – Detection of antibodies attacking bone marrow cells.
- Assessment of nutrient and hormone levels – Analysis of factors influencing blood cell production.
Regular check-ups are crucial to monitoring the course of the disease and preventing complications.
MONTHLY SET NAD + -> Energy and Vitality Boost
Treatment of aplastic anemia
The choice of therapy depends on the stage of the disease, the patient's age, and their general health. The main goals of treatment are to restore blood cell production and relieve symptoms. Treatment methods include:
- Observation and monitoring – In mild cases, regular medical monitoring may be sufficient.
- Immunosuppressive therapy – Inhibits autoimmune response, improving bone marrow function.
- Bone marrow transplant – Often used in severe cases, especially in patients who are resistant to other forms of therapy.
- Blood transfusions – Temporarily increase blood cell counts and reduce the risk of complications related to anemia.
- Supportive treatment – Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications may be used for infections and other complications.
Thanks to medical advances, aplastic anemia treatment strategies are constantly evolving, which increases the chances of effective therapy. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment significantly improve the quality of life and prognosis of patients affected by this blood disease.