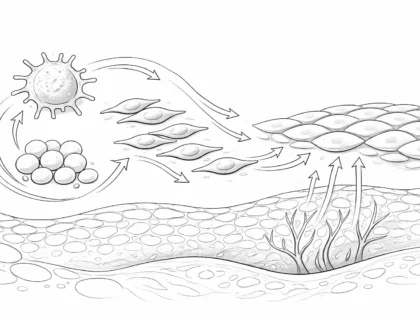
How Cell Signaling Compounds Communicate Inside the Body
-
PepEurope
- Posted on
- 0 comments
Why Understanding Cell Signaling Compounds Matters ? Every second, trillions of cells inside the human body must communicate accurately to maintain balance, respond to changes, and support life. When this communication fails, biological systems lose coordination.
This is where cell signaling compounds play a crucial role. They act as precise chemical messengers that allow cells to send, receive, and interpret information efficiently. Understanding how these compounds work provides clarity on one of the most fundamental processes in biological communication.
What Are Cell Signaling Compounds?
Cell signaling compounds are specialized chemical messengers also known as ligands that enable communication between cells. These molecules are released by one cell and recognized by another through specific receptors, triggering a controlled response inside the target cell.
Without cell signaling compounds, cells would act independently, making organized biological processes impossible. Their specificity ensures that messages are delivered accurately, even within highly complex biological systems.
Key characteristics:
- High specificity between signal and receptor
- Ability to trigger intracellular pathways
- Role in maintaining biological coordination
How Cell Signaling Compounds Communicate Inside the Body
Signal Stages & Cellular Outcome
|
Stage |
What Happens |
Why It Matters |
| Reception | Ligand binds to specific receptor | Ensures signal specificity |
| Transduction | Signal is relayed and amplified | Converts external signal into action |
| Response | Cellular change occurs | Enables adaptation, growth, survival |
| Termination | Signal is shut down | Prevents overstimulation |
Cell signaling follows a structured three-stage process that ensures clarity and control in biological communication.
Sema Beauty & Slim (weight control / healthy skin)
Sema Metabolic Boost (Appetite / Metabolism / Energy)
Metabolic Boost Duo (Appetite Suppression / Energy / Metabolism)
Sleep and Slim Pack (weight control / sleep regeneration)
Signal Reception
The process begins when a signaling compound binds to a receptor on or inside the target cell. Water-soluble signals typically interact with receptors on the cell surface, while lipid-soluble compounds can enter the cell and bind to intracellular receptors. This specificity ensures only the correct cells respond.
Signal Transduction
Once the receptor is activated, the signal is relayed through a cascade of molecular events inside the cell. This stage often amplifies the original message, allowing a small signal to create a significant cellular response. Second messengers such as calcium ions or cyclic molecules help distribute the signal rapidly.
Cellular Response
The final stage is the response, where the cell adjusts its activity. This can involve changes in gene expression, metabolism, structure, or function. Afterward, termination mechanisms ensure the signal does not remain active longer than necessary.
This system solves a key biological problem:
How cells respond quickly and accurately without constant external control.
Sema Beauty & Slim (weight control / healthy skin)
Sema Metabolic Boost (Appetite / Metabolism / Energy)
Metabolic Boost Duo (Appetite Suppression / Energy / Metabolism)
Sleep and Slim Pack (weight control / sleep regeneration)
Types of Biological Communication in Cell Signaling
Cell signaling compounds operate through different communication methods depending on distance and purpose. Long-distance signaling allows coordination across the body, while short-distance signaling supports localized responses. Direct contact signaling ensures precision where immediate interaction is required.
Main signaling types:
- Endocrine (long-distance communication)
- Paracrine (local signaling)
- Autocrine (self-signaling)
- Direct cell-to-cell contact
This layered approach ensures biological flexibility and adaptability.
Types of Cell Signaling Compounds & How They Communicate
Signaling Compound Type | Primary Function | Distance Traveled | Receptor Location | Example Compounds |
| Hormones | Coordinate long-term biological responses | Long-distance (endocrine) | Cell surface or intracellular | Insulin, Estrogen |
| Neurotransmitters | Enable rapid cell-to-cell communication | Very short distance (synapse) | Cell surface (ion channels, GPCRs) | Acetylcholine, Dopamine |
| Growth Factors | Regulate cell growth and division | Local (paracrine) | Cell surface (RTKs) | EGF, PDGF |
| Local Mediators | Trigger immediate localized responses | Local (paracrine/autocrine) | Cell surface | Histamine, Prostaglandins |
| Gaseous Signals | Rapid intracellular signaling | Very short | Intracellular | Nitric Oxide (NO), H₂S |
| Ions (Second Messengers) | Amplify intracellular signaling | Inside the cell | Cytosol / organelles | Calcium (Ca²⁺) |
Sema Beauty & Slim (weight control / healthy skin)
Sema Metabolic Boost (Appetite / Metabolism / Energy)
Metabolic Boost Duo (Appetite Suppression / Energy / Metabolism)
Sleep and Slim Pack (weight control / sleep regeneration)
Major Classes of Cell Signaling Compounds
Cell signaling compounds vary in structure and function, allowing them to serve different biological roles. Proteins and peptides often regulate growth and metabolism, while lipid-based compounds easily cross membranes. Gaseous and ionic messengers enable rapid intracellular signaling.
Key categories:
- Proteins and peptides
- Lipid-derived molecules
- Gases such as nitric oxide
- Ions like calcium
Each class contributes uniquely to biological communication.
Key Cell Signaling Pathways Explained Simply
Cells rely on established signaling pathways to interpret messages accurately. G protein-coupled receptors translate signals into intracellular actions. Receptor kinases activate cascades that regulate growth and division. Ion channels adjust electrical and chemical gradients, while second messengers amplify signals internally. These pathways ensure signals are converted into precise cellular outcomes.
Why Cell Signaling Compounds Are Essential for Life
Cell signaling compounds regulate nearly every biological process, from energy management to cellular renewal. They allow tissues to grow, adapt, and maintain balance within changing environments. Without these compounds, cells would lack coordination, leading to biological instability.
Their importance:
- Regulating metabolism and energy flow
- Supporting growth and cellular renewal
- Enabling adaptive biological responses
What Happens When Cell Signaling Is Disrupted
When signaling pathways malfunction, communication errors occur. Signals may become too strong, too weak, or misdirected. This disruption affects cellular balance and highlights why accurate signaling is essential for healthy biological function. Understanding signaling mechanisms helps researchers identify where communication breaks down.
Cell Signaling Compounds in Modern Biological Research
In biological and biochemical research, cell signaling compounds are studied to better understand how cells respond to stimuli. Research-focused organizations like PepEurope Ltd support this exploration by emphasizing scientific integrity, quality standards, and transparency. This commitment strengthens trust and supports evidence-based biological discovery.
Sema Beauty & Slim (weight control / healthy skin)
Sema Metabolic Boost (Appetite / Metabolism / Energy)
Metabolic Boost Duo (Appetite Suppression / Energy / Metabolism)
Sleep and Slim Pack (weight control / sleep regeneration)
FAQs
What are cell signaling compounds in simple terms?
Cell signaling compounds are chemical messengers that allow cells to communicate with one another. They are released by a signaling cell and detected by a target cell through specific receptors. Once detected, they trigger a series of internal reactions that tell the cell how to respond. This communication ensures cells act in a coordinated way rather than independently. Without these compounds, essential biological processes such as growth, adaptation, and regulation would not function properly.
How do cells know which signal to respond to?
Cells respond to signals through receptor specificity. Each cell has receptors designed to recognize certain signaling compounds based on molecular shape and chemical properties. When the correct signal binds, it activates that receptor and initiates a response. Signals that do not match the receptor are ignored. This mechanism prevents confusion and ensures that messages reach only the intended target cells, maintaining accuracy in biological communication.
What is the difference between hormones and cell signaling compounds?
Hormones are a specific type of cell signaling compound that travel long distances through the bloodstream to reach target cells. Cell signaling compounds is a broader term that includes hormones, neurotransmitters, local mediators, ions, and gases. While all hormones are signaling compounds, not all signaling compounds are hormones. This distinction highlights the diversity of biological communication mechanisms.
Why are receptors essential in cell signaling?
Receptors are essential because they allow cells to detect and interpret signaling compounds. Without receptors, signals would have no effect. Receptors ensure specificity, trigger intracellular pathways, and regulate signal strength and duration. They also help terminate signals once the response is complete. This control prevents overstimulation and maintains cellular balance.
Are cell signaling compounds present in all living organisms?
Yes, cell signaling compounds are found in all living organisms, from simple single-celled life forms to complex multicellular organisms. While the complexity of signaling systems varies, the fundamental principle of chemical communication is universal. This highlights the evolutionary importance of signaling compounds in maintaining life and biological organization.
Conclusion
Cell signaling compounds form the foundation of biological communication, enabling cells to coordinate actions, adapt to change, and maintain balance. By understanding how these compounds work from reception to response we gain insight into one of biology’s most essential systems. For researchers and learners alike, exploring cell signaling compounds offers a clearer view of how life operates at the cellular level.