Melasma: Causes, Treatments, and How to Deal with It Naturally
-
PepEurope
- Posted on
- 0 comments
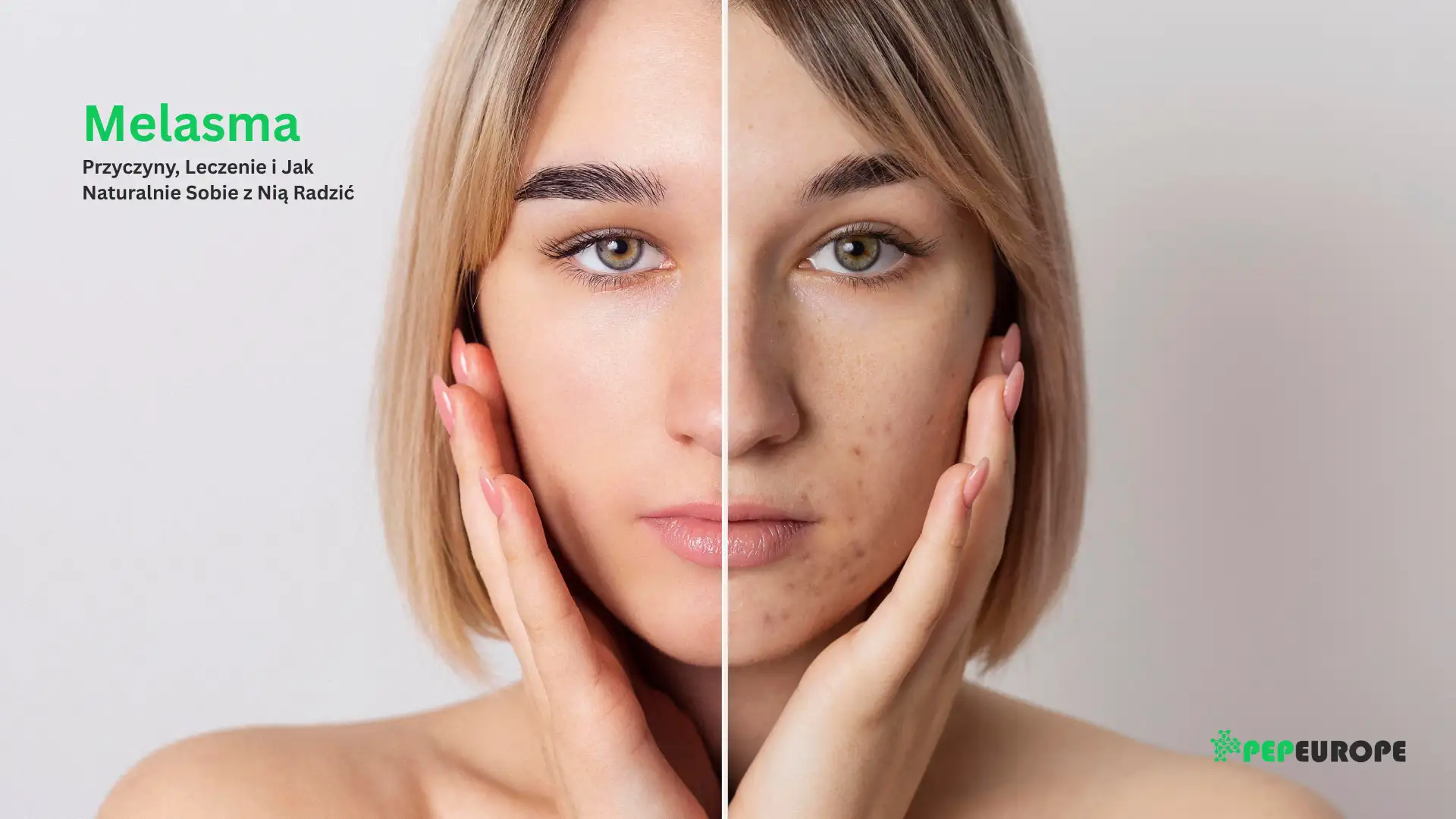

Learn what melasma is, its causes, and effective treatments—both medical and natural. Learn how to control melasma and prevent its recurrence with simple skin care tips.
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes dark, discolored patches to appear on the skin, most often on the face. While it is not harmful or painful, many people find it frustrating because it affects their appearance and self-confidence. In this article, we will discuss what it is, what causes it, and how it can be treated or controlled both musically and naturally.
What is Melasma?
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation that means your skin produces too much melanin in certain areas, resulting in darker spots or discolorations. These spots are usually brown or gray-brown and most often appear on the cheeks, forehead, nose, chin, and upper lip. In some cases, it can also appear on other parts of the body, such as the neck or forearms, especially after sun exposure.
Who Is Most At Risk?
Melasma affects both men and women, but is much more common in women, especially during pregnancy, when it is often called the “mask of pregnancy.” People with darker skin (such as Latinx, Asian, or Middle Eastern descent) are more likely to develop melasma because of naturally higher levels of melanin in their skin.
What Causes Melasma?
The exact cause of melasma is not always clear, but several triggers and risk factors are known:
- Sun exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation can trigger melanin production, worsening melasma.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone therapy can affect melasma.
- Genetics: A family history of melasma increases the risk of its occurrence.
- Skin care products: Some products may irritate the skin and cause flare-ups.
- Warmth and light: Even heat or visible light (not just UV) can trigger melasma in some people.
Common Treatments for Melasma
It can be persistent and may take time to go away. Fortunately, there are various treatments available depending on the stage of the disease:
- Local Creams
Dermatologists often prescribe creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, tretinoin, azelaic acid, or kojic acid to help gradually lighten spots.
- Chemical Peels
A dermatologist may use a chemical solution to exfoliate the top layer of skin, helping it regenerate and reduce discoloration.
- Laser Therapies or Light Therapy
Advanced treatments such as fractional lasers, IPL (intense pulsed light) or Q-switched lasers can reach deeper layers of pigment, but results are variable and must be performed carefully to avoid aggravating the skin.
- Micro-needling
This technique stimulates collagen production and can help improve pigmentation when performed by a qualified professional.
Natural Ways to Cope
For those looking for gentler alternatives, here are some natural tips that can help control or reduce melasma:
– Sun Protection Is A Must
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) every day, even indoors. Reapply every 2 hours when outdoors. Sun exposure is a major trigger, so hats and sunglasses are also essential.
– Aloe Vera Gel
This soothing plant extract contains aloin, which may help lighten discoloration over time.
– Licorice Extract
Licorice root is known for its natural skin brightening properties and is a common ingredient in melasma-friendly cosmetics.
– Vitamin C Serum
Vitamin C helps brighten the skin and reduce melanin production. It also protects the skin from oxidative stress.
– Healthy Diet
Eating foods rich in antioxidants (such as berries, green leafy vegetables and nuts) can support skin health and reduce stress oxidative.
Can It Disappear On Its Own?
In some cases, especially when it is hormonal (e.g. after pregnancy), melasma can disappear naturally after the hormone levels have normalized. However, for many people it is a long-term condition that requires consistent care and control.
When to See a Dermatologist
If you are unsure whether the dark spots on your skin are melasma or another condition (e.g. post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or even melanoma), it is always best to see a dermatologist for a professional diagnosis and treatment plan.
Summary
It’s a persistent skin condition, but with the right approach, it can be effectively controlled. Whether you choose medical treatment, natural methods, or a combination of both, consistency and sun protection are key. Every skin is different, so finding the right solution may take time, but improvement is possible.